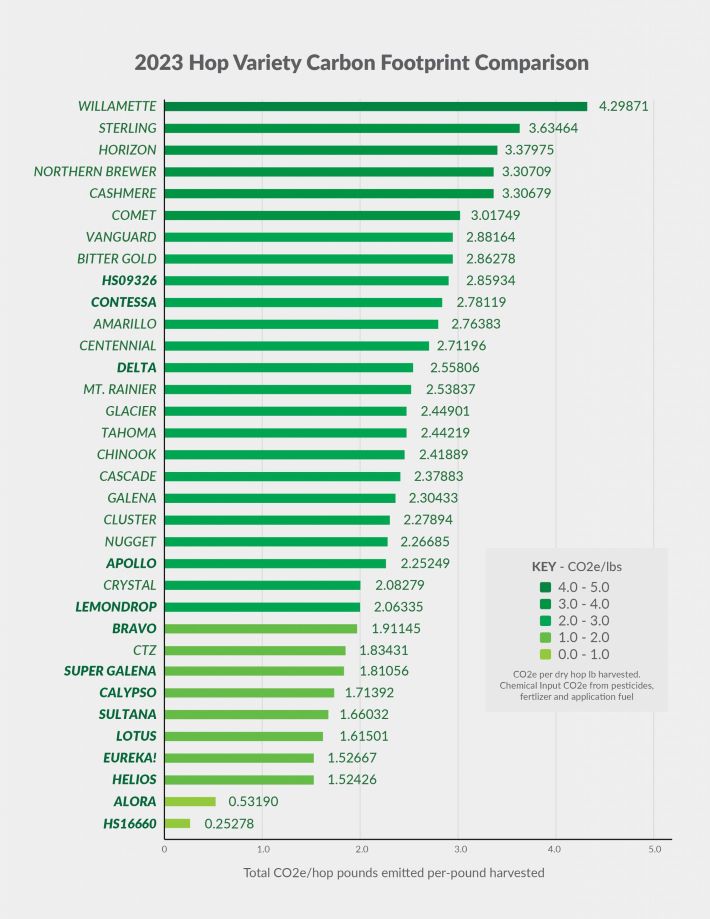
Hopsteiner has updated a list of the CO2 equivalent emissions (CO2e) of 34 hop cultivars it grows on its farms. Greenhouse gas emissions are associated with the formulation, packaging, and application of multiple inputs, such as such as water, fertilizer, pesticides, and fuel. Hopsteiner measured these inputs by compiling hop production records, cone yields, and alpha-acid yields across multiple varieties to determine the carbon footprint associated with each variety.
This list tracks Hopsteiner proprietary (in bold) as well as public varieties, but not every public variety and not many other proprietary varieties. Those include four of the most grown American varieties — Citra, Mosaic, Simcoe, and HBC 682.
Comparing the new list to one from 2021 illustrates that emissions are crop year dependent. This is agriculture.
Doug Wilson, Hopsteiner director of sales and marketing, cautions that data for Alora and HS16660 is based on limited data. Alora was still an experimental variety last year, so acreage is limited. HS16660 is still experimental, grown in a five-acre yard. Both, however, were selected for disease resistance and yield — two important qualities to lower (CO2e).
Related: Some hops are ready for climate change; some are not.